- What is a trial?
- What do you need to prepare for trial?
- How do you apply for subpoena for witnesses?
- What are the stages for trial?
- What if you do not agree with the court's judgment?
1) What is a trial?
A trial is conducted for parties to present their case (their witnesses and evidence) before the trial magistrate who will then determine liability.
2) What do you need to prepare before a trial?
Trial preparation includes as follow:
- Compiling all relevant documents in a chronological order into a bundle (known as 'bundle of documents');
- Compiling the list of witnesses whom you intend to call to give evidence for your case.
- Apply for subpoena for witnesses;
- Prepare Affidavits of Examination in Chief for witnesses i.e. an affidavit consisting of the witness's evidence for trial which is within the witness's knowledge and belief. This also applies to the bundle of documents. The affidavit must be sworn before a commissioner of oath.
- Compile all the relevant cases and laws you are relying on for your case (known as 'bundle of authorities').
3) How do you apply for subpoena for witnesses?
You may apply for subpoena during the pre-trial conference before the trial Magistrate or via a letter. The fee for issuing a subpoena is $10 per subpoena. Parties may seek assistance from the court's process server to serve the subpoena on the witness.
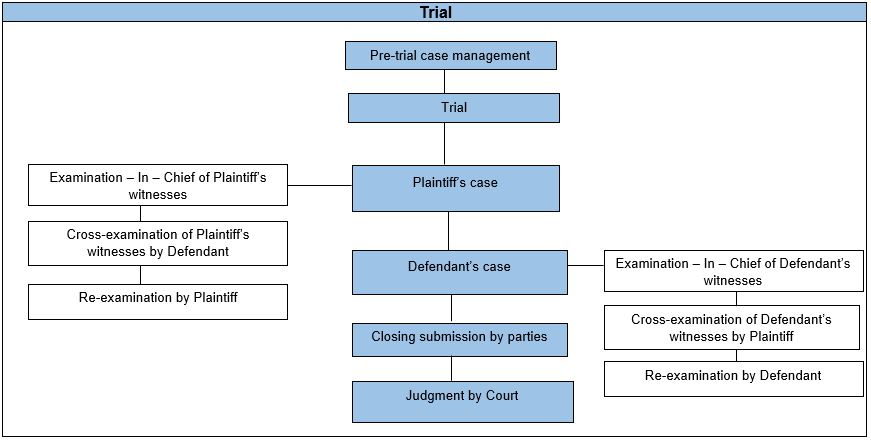
4) What are the stages of a trial?
The trial will be in the following order:
| Pre-trial Case Management | Directions will be given by the court for parties to exchange and file their bundles (bundle of documents, bundle of affidavits, bundle of authorities) |
|---|
Plaintiff's case
| Plaintiff witnesses will take turns to testify in court. Witnesses may use their sworn affidavit as evidence in court. This affidavit must be read in open court. They will be subject to Cross-examination by the Defence. Witnesses may refer to documents in the 'bundle of documents'. After each witness, the Defendant will be given opportunity to question (cross-examine) the witnesses.
|
|---|
Defendant's case
| Similar process applies to the Defence case – Defendant present their evidence through witnesses and documents etc. |
|---|
| Closing submission by parties | Parties summarize their case and submit why the court should determine in their favour based on the evidence presented and the applicable laws and cases. Parties may submit 'bundle of authorities' at this stage. |
|---|
Judgment by Court
| Court delivers their decision/judgment including any order on cost.
|
|---|
5) What if you do not agree with the court's judgment?If a party does not agree with the court's judgment, they can appeal their case to the High Court. They have within one month from the date of judgment to do so. See '
Appeal' for procedure.

